Introduction
Choosing the right component for your hydraulic system, whether it be a tube, pipe, or hose, is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Each component has unique characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages that make them suitable for different applications and environments. This blog post will guide you through understanding these components, their applications, and how to select the best option for your specific needs.
The Differences Between Tubes, Pipes, and Hoses
In hydraulic systems, tubes and pipes are frequently discussed together due to their fundamental role as rigid conduits for fluid power transmission. Although tubes are typically specified by their precise outer diameter and wall thickness for exact routing and connections, and pipes are defined by a nominal pipe size and schedule for flow capacity, their functional application in hydraulics often overlaps. It is important to note that, for engineers, flow rate is the most important measurement to consider when deciding the size of the tube or pipe needed in their hydraulc system.
Both are engineered for fixed installations where robust, static pathways are required, capable of withstanding significant pressure, temperature, and mechanical stresses. They are commonly fabricated from various grades of steel (such as carbon or stainless steel) or other alloys, chosen for specific properties like corrosion resistance or high-pressure capability. This shared characteristic of rigidity and suitability for permanent, static applications is why, for the remainder of this discussion, we will group tubes and pipes as a single category of hydraulic component.

Conversely, hydraulic hoses are the flexible counterpart to rigid tubes and pipes. While also serving as a conduit of hydraulic fluid, the key difference is flexibility. Hoses are essential for flexible applications where components move relative to each other, or where installation space is constrained. A hydraulic hose is a composite structure, typically featuring an inner liner (often thermoplastic or synthetic rubber for fluid compatibility), one or more high-strength reinforcement layers (like braided or spiral-wound steel wire for pressure integrity), and a robust outer cover to protect against abrasion and environmental elements. This multi-layered design allows hoses to not only withstand the high pressures common in hydraulic systems, but also to absorb vibrations, dampen noise, and be routed easily around obstacles, providing a versatile solution where rigidity is impractical.

Tubes and Pipes are the preferred choice for hydraulic systems demanding precision, durability, and a static, robust fluid pathway. Their inherent rigidity, coupled with precise manufacturing and material strength, makes them exceptionally suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure environments where maintaining consistent dimensions and minimal expansion under load is critical for system efficiency and control. As tubes can be formed to fit specific layouts, their fixed nature makes them ideal for permanent installations.
Their critical applications span various heavy industries:
- In the construction industry, tubes and pipes are fundamental to heavy machinery like excavators, cranes, and concrete pump trucks, reliably transmitting hydraulic oil and pressure to ensure precise and powerful operation under demanding conditions.
- Within marine machinery, they provide the essential stability and reliability for high-pressure, high-torque systems such as steering gear, lifting equipment, and propulsion, where robust, fixed connections are essential.
- For the oil and gas industry, large-diameter pipes are indispensable for long-distance transport of crude oil and natural gas, engineered to endure extreme pressures and harsh environmental challenges.
- In chemical processing, their material integrity and corrosion resistance are vital for the safe and secure transport of corrosive and hazardous materials within static plant infrastructures.
Hydraulic hoses are indispensable where flexibility, mobility, or vibration isolation is a system requirement. Their composite construction allows them to excel in dynamic applications where components are in motion, or in tight spaces where rigid installations would be impractical.
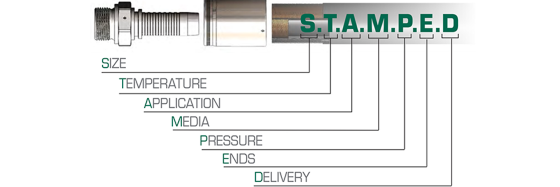
The selection of the appropriate hose is systematically guided by the STAMPED method, ensuring optimal performance:
- Size: Matching internal and external diameters for flow and fit.
- Temperature: Verifying tolerance to both fluid and ambient temperatures.
- Application: Considering specific use, flexing cycles, and environmental factors like abrasion.
- Media: Confirming chemical compatibility with the hydraulic fluid.
- Pressure: Ensuring the hose meets system working and burst pressure demands.
- Ends: Selecting the correct fittings for secure connections.
- Delivery: Factoring in availability and lead times.
Hoses are widely used in many different industries and applications due to their adaptability:
- In agriculture, they are crucial for irrigation systems, sprayer booms, and various machinery, designed to withstand chemical exposure and constant flexing in the field.
- In the automotive industry, hoses are vital for systems like brake lines, power steering, and fuel delivery, accommodating pressure fluctuations and dynamic movement within confined engine bays and chassis.
Advantages of Tubes and Pipes
- Durability and Strength: Can withstand significant mechanical stress, high pressures, and high temperatures without deforming, ensuring consistent fluid flow.
- Minimal Expansion: Exhibit very low volumetric expansion under pressure, which is crucial for precise control and responsiveness in hydraulic systems.
- Long Lifespan: Generally, offer a longer service life compared to flexible hoses due to their robust construction and resistance to external wear.
- Consistent Dimensions: Maintain stable internal and external dimensions under varying operating conditions.
- Heat Dissipation: Excellent conductors of heat, aiding in the cooling of hydraulic fluid.
- Corrosion Resistance: Many materials, especially stainless steel, offer superior resistance to corrosion in harsh environments.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of fixed installations from plumbing to heavy industrial applications and can be custom bent to fit complex system environments.
Disadvantages of Tubes and Pipes
- Limited Flexibility: Their rigidity makes installation in tight or complex spaces challenging, often requiring precise bending and specialized tools.
- Installation Complexity: Installation can be time-consuming and costly, requiring skilled labor and specific bending and fitting equipment to ensure secure, leak-free connections. Misalignment can lead to system failures.
- Vibration Transfer: Efficiently transfer vibrations throughout the system, potentially leading to noise, fatigue, and loosening of connections over time, especially in high-vibration environments.
- Length Limitations: Typically available in fixed lengths, which may necessitate additional fittings and connections for longer runs, increasing potential leak points.
- Thermal Expansion/Contraction: Can expand and contract with temperature changes, potentially stressing connections and requiring expansion joints in very long runs.
- Susceptibility to External Damage: Can be susceptible to damage from external forces like impacts or ground movement in exposed installations.
Advantages of Hoses
- Superior Flexibility: Can easily bend, maneuver around obstacles, and accommodate relative motion between components, making them ideal for applications with limited space or dynamic movement.
- Vibration and Noise Absorption: Effectively absorb system vibrations and dampen noise, reducing wear and tear on components and improving operator comfort.
- Longer Continuous Lengths: Available in much longer continuous lengths than rigid conduits, reducing the need for multiple connections and potential leak points.
- Ease of Customization: Readily available with a wide range of lengths, materials, sizes, and end fittings for tailored solutions.
- Easier Installation: Generally simpler and quicker to install in complex layouts compared to rigid tubing, requiring fewer specialized tools for routing.
Disadvantages of Hoses
- Abrasion Susceptibility: The outer cover is prone to abrasion, which is a common cause of hose failure if not properly protected or routed.
- Limited Temperature Range: Each hose type has specific temperature limits; exceeding these can lead to degradation of materials and premature failure.
- Prone to Leaks: Due to their flexible nature and multiple layers, they can be more prone to leaks than rigid pipes/tubes, especially at connection points or if damaged.
- Weight: Can be heavier than some rigid alternatives, which might be a consideration in weight-sensitive applications.
- Pressure Limitations: While high-pressure hoses exist, very high pressures may still sometimes favor rigid tubing for stability and safety.
- Degradation Over Time: Materials can degrade due to exposure to chemicals, ozone, UV, and continuous flexing, leading to a shorter lifespan compared to rigid conduits.
- Working Environment:
- Tubes/Pipes: Ideal for high-temperature settings, high mechanical stress, or static installations where stability and resistance to deformation are critical.
- Hoses: Essential for applications involving constant movement, significant vibration, or intricate routing in confined spaces.
- Type of Hydraulic Fluid:
- Ensure the conduit material is compatible with the specific hydraulic fluid to prevent degradation, corrosion, and maintain leak-tightness. Certain fluids may require specialized materials (e.g., specific hose liners, stainless steel tubing).
- System Pressure:
- Tubes/Pipes: Generally preferred for very high-pressure applications where robust stability and minimal volumetric expansion are paramount.
- Hoses: Excellently suited for systems with pressure fluctuations, where their flexibility helps absorb surges and maintain integrity.
- Space Availability:
- Hoses: Offer maximum flexibility for routing in extremely confined spaces or around numerous obstacles.
- Tubes/Pipes: Provide some bending capability for custom routes, requiring less space than straight pipes but more than hoses.
- Material Choice:
- Select materials (e.g., various steels, specialized thermoplastics) based on specific application requirements like corrosion resistance, temperature range, or chemical compatibility.
- Amount of Bend or Movement Needed:
- Hoses: Provide the greatest flexibility for dynamic motion and custom lengths, accommodating significant movement.
- Tubes/Pipes: Can be custom bent for specific static routes, offering adaptability.
Conclusion
The choice between tubes, pipes, and hoses depends on various factors, including the working environment, type of fluid, pressure requirements, and space availability. By carefully considering these factors and understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each component, you can make an informed decision that ensures the efficiency and reliability of your hydraulic system. Whether you need the precision of tubes, the durability of pipes, or the flexibility of hoses, selecting the right option will help you achieve optimal performance in your application.
What is the difference between a hydraulic tube, pipe, and hose?
The key differences between a hydraulic tube, pipe, and hose are their flexibility and application suitability. Hydraulic hoses are flexible for dynamic systems with movement and vibration, while hydraulic tubes and pipes are rigid, used for high-pressure, fixed pathways in static hydraulic systems.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a hydraulic hose?
When selecting a hydraulic hose, it's crucial to consider key factors like size, temperature, application, media, pressure, and ends. Using a methodical approach like the "STAMPED" method ensures you choose the right hose to prevent failures and optimize system performance.
How do I choose the right hydraulic component (tube, pipe, or hose) for a specific applications?
To choose the right hydraulic component, you must match the component's characteristics to the application's needs. For static, high-pressure lines in heavy machinery like excavators and cranes, tubes and pipes are the best choice, while flexible hydraulic hoses are better for dynamic applications like brake lines in the automotive industry or sprayer booms in agriculture.
What are the main advantages and disadvantages of using hydraulic tubes and pipes?
The main advantages of hydraulic tubes and pipes are their durability, ability to withstand high pressure, and long-term stability. Their disadvantages include difficult installation, lack of flexibility, and a tendency to transfer noise and vibration through the system.
When should I use hydraulic hoses instead of tubes or pipes?
You should use hydraulic hoses instead of tubes or pipes in applications requiring flexibility, such as in the automotive industry for brake lines and power steering, or on agricultural sprayer booms, where components are in motion and vibration absorption is necessary.

Subscribe to the STAUFF Newsletter
Get the latest news and updates from us at STAUFF right to your inbox!













